

The world of “non-plastics”: Come and & Explore with Tion
In our modern world, Plastics is used in every single element in our daily life, well almost!
However, littering and non-considerate usages have created a major problem in our ecology, as plastics may take years to degrade naturally.
So, how can we take a step forward to minimize the risk of harming our earth? Is there any way?
The good news is YES! Let us take you to the tour of Environment friendly polymers i.e., our Bio-compostable polymers or one can say Bio-degradable or Bio-plastics.
Before, that, a short course in the definitions/terms.
What is polymer?
A chemical compound made from small molecules that is arranged in a simple repeating unit to form a larger molecule is called Polymers.
Difference between “Normal” plastics and “Bio-degradable/Bio-compostable” plastics:
| Normal conventional Plastics | Bio-compostable Plastics |
|---|---|
| - Conventional plastics are derived from fossil fuels or natural gases. These plastics are also called petroleum-based polymers. | - These plastics are produced from renewable resources vegetable fats, oils, Corns, Potato starch, Topiocca, recycled food wastes etc. |
| - These plastics are not derived from natural resources. | - Bio-plastics are usually derived from sugar derivative including starch, cellulose and lactic acid. |
| - These plastics doesn’t decompose it might stay in environment for more than 100-200 years. | - These polymers decompose in certain period of time i.e., 6 months to 1 year. |
| - Likely to causes environment, health damages due to pollution and it also harmful for marine lives, unless recycled and re-used. | - Doesn’t cause harm to the environment. |
| - Eg. PE, PP, LLDPE, PS etc. | - Eg. PLA, PBAT etc. |
Overview of types of Plastics:
- Biodegradable plastics: These plastics biodegrade in a specific medium (water, soil, compost) under certain conditions and in varying periods of time.
- Industrially compostable plastics: These plastics biodegrade in the conditions of an industrial composting plant or an industrial anaerobic digestion plant with a subsequent composting step.
- Home compostable plastics: These types of plastics biodegrade in the conditions of a well-managed home composter at lower temperatures than in industrial composting plants. Most of them also biodegrade in industrial composting plants.
- Bio-based plastics: These plastics are fully or partly made from biological raw materials as opposed to the fossil raw material (oil) used in conventional plastics.
- Non-biodegradable plastics: These plastics last for long periods of time. They can disintegrate into smaller pieces, forming microplastics, and accumulate in the environment.
- Oxo-degradable plastics: These plastics include additives that, through oxidation, lead to their fragmentation into microplastics or chemical decomposition.
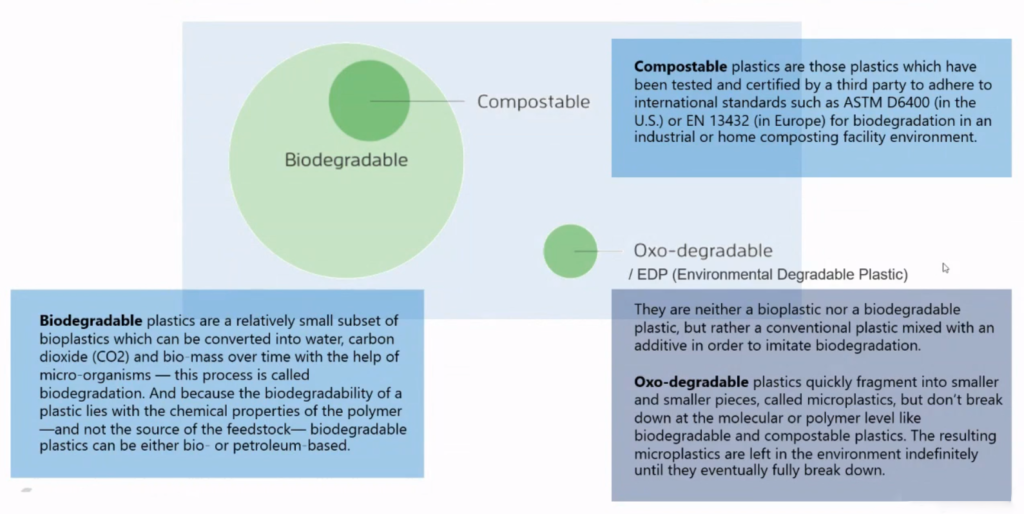

Fig. 1) This fig. shows that all compostable Polymers can be Bio-degradable polymers but not all Bio-degradable polymers are compostable polymers, Oxo-degradable polymers are neither Bio-degradable nor compostable polymers.
Bio-compostable/Bio-degradable polymers Applications:
These polymers are used in many areas of our daily life, some of these are as mentioned below,
- Packaging – Shopping/carry bags, compostable collection bags etc. to substitute many single use plastics
- Used to make disposable catering service wares.
- Mulch films (Agriculture)
- Paper coating
- Injection molding
- Used in medical dept to make screws, pins, etc.
- Consumer goods etc.
Bio-compostable/Bio-degradable polymers Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
- These plastic products are broken down by bacteria that process occurs naturally once products comes in contact with environment.
- Reduction in emission of Greenhouse gases.
- Compostability
- Lower petroleum consumption
- Reduction in amount of waste produced
- Reduction in carbon emission
- Les landfill area needs (as plastics can be absorbed by the soil and converted to compost).
- Recyclable
Disadvantages:
- Cost is high as compare to conventional plastics
- Need of composters
- Engineering issues
- Risk of contaminations
Current Market scenario of Bio-compostable/Bio-degradable Polymers:
The global bio-degradable plastic market size was estimated at USD 4.1 billions in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 4.6 billion in 2022. Key factors that driving these plastics market growth include governments prohibiting the use of single-use plastic coupled with rising awareness among the public regarding the ill-effects of plastic waste.
Future growth of Bio-compostable polymers:
There is no. of large and small firms, who have begun to invest in the field of bio-degradable and Bio-compostable polymers.
The global market of Bio-degradable/Bio-compostable polymers are expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.7%from 2022 to 2030 to reach USD 10.0 billion by 2030.
This will be a growth market, according to the market study ‘Biodegradable Polymers: Past, Present, and Future’ by The Society for Engineering in Agriculture, Food and Biological Systems. Who states that “There are a seemingly limitless number of areas where biodegradable polymer materials may find use in sectors such as agriculture, automotives, medicine, and packaging all require environmentally friendly polymers, Because the level of biodegradation may be tailored to a specific need, each industry is able to create its own ideal material.
The various modes of biodegradation are also a key advantage of such materials, because disposal methods may be tailored to industry specifications. Environmental responsibility is constantly increasing in importance to both consumers and industry.”
Join us in the Exhibition of BioPlastex2022, Bengaluru, there you will know more about our Environment friendly polymers. Link is as follow www.bioplastex.com, see you at Booth No. 20
Let’s create together, a beautiful world, for all…


Article Source & references:
- https://www.conserve-energy-future.com/advantages-disadvantages-uses-biodegradable-plastics.php
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/biodegradable-plastics-market
- https://earth911.com/business-policy/bioplastics-biodegradable-plastics-compostable-plastics/
- https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/biodegradable-and-compostable-plastics
- https://blog.spotchemi.com/the-market-for-biodegradable-and-biobased-polymers-and-plastics/
